The Need for Additional Water Storage

(The below article is reproduced from the January, 2022 issue of Oregon Cattleman, the publication of the Oregon Cattlemen’s Association. For a PDF copy of the article, use this link.)
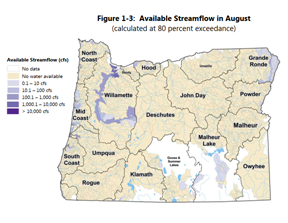
2021 was a terrible water year in Oregon. We experienced record high temperatures and record low precipitation, after several years of already below-average precipitation, little or no carryover water in reservoirs, historically dry soils, and severe wildfires. This year highlighted the need for additional water storage to increase water security during times of drought.
At the Oregon Cattlemen’s Association’s annual meeting, the Water Resources Committee voted to adopt a resolution promoting water infrastructure and storage to guide the organization’s priorities going forward, and the Board adopted the resolution. This policy will be especially important in coming years, as we face increasing roadblocks to achieving water storage and infrastructure goals. State water policies are oftentimes conflicting, recognizing the importance of creating additional storage, while at the same time promoting activities that foreclose opportunities for storage.
For example, Oregon’s Integrated Water Resources Strategy includes a “recommended action” to plan and prepare for drought resiliency. The Strategy also includes a “recommended action” to develop instream water protections. These two strategies are not necessarily opposed, however, when one strategy is actively pursued while the other falls by the wayside, the State’s actions do not balance both needs. Moreover, only so much water exists within water basins, and the creation of instream water rights takes that water “off the table” for purposes of increasing or creating water storage.
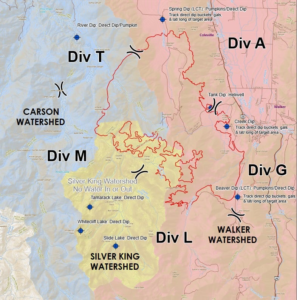
In 1987, the Oregon State Legislature passed the Instream Water Right Act allowing the State to convert minimum perennial instream flows to instream water rights, apply for new instream water rights, and lease or transfer existing water rights to instream uses such as recreation, pollution abatement, and fish and wildlife. Thus, instream water rights are not a new concept. However, the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife’s (ODFW’s) website details that the agency “re-established” its instream water rights filing program in 2016, “consistent with Oregon’s Integrated Water Resources Strategy.” Thus, we have seen in the last few years hundreds of applications for instream water rights filed by ODFW in different water basins throughout the State. ODFW’s policy stated in its administrative regulations is “to obtain an in-stream water right on every waterway exhibiting fish and wildlife values.” OAR 635-400-0005.
Unlike appropriative water rights, instream water rights are not constrained by the amount of water actually available to fulfill the instream water right. Rather, ODFW’s applications may request the amount of water ODFW determines is needed to support the fish and/or wildlife species. As such, ODFW applications regularly include requested rates that exceed available stream flows. Such applications, if approved, have the effect of precluding any new appropriative water use rights within or upstream from the stream reach designated in the application.
Moreover, once instream water rights are in place, existing water right holders lose the flexibility to transfer their points of diversion upstream. The instream water right holder (the State) must consent to the “injury” the transfer would cause. In exchange for its consent, the State typically requires mitigation by placing a portion of the transferred water rights instream. The 1987 Instream Water Right Act provided, “The establishment of an in-stream water right…shall not take away or impair any permitted, certificated or decreed right to any waters or to use of any waters vested prior to the date the in-stream water right is established…” ORS 537.334(2). In practice, however, existing water right holders lose the flexibility they might have otherwise enjoyed to modify their water rights as needed for their operations.
This is not to say that instream water rights have no place or value. The reason for outlining the increased emphasis on instream rights recently, and the effects such rights have on new and existing appropriative water rights, is to point out that we, as a State, are falling short on drought resiliency preparation efforts at the same time water resources are being irreversibly committed to instream purposes. In 2013, when the Legislature passed Senate Bill 839, establishing the Water Supply Development Fund, many hoped that the fund would be used to increase water storage throughout the State. As a whole, that fund has not created substantial new storage. The State must do better to carry forward all components of the Integrated Water Resources Strategy, including planning and preparation for drought resiliency through water storage and infrastructure improvements.
The Oregon Water Resources Department (OWRD) received a large funding package in the 2021 regular session of the Legislature. The Oregon Cattlemen’s Association joined a coalition letter to OWRD outlining recommended priorities for implementing that funding. The first priority in that letter is a request that OWRD renew its focus on increasing storage and improving disaster resiliency. Congress recently passed the Infrastructure Investment Jobs Act, and the letter further asks OWRD to develop a plan to leverage federal funds in support of these efforts.
In addition to government reprioritization and implementation of plans to prepare for droughts, individuals and groups from the agriculture community will need to lead the way and identify projects in their communities. It is possible that storage opportunities may be identified through place-based planning efforts in partnership with State agencies. Soil and water conservation districts and other local entities can also assist individuals to navigate the myriad of questions and processes involved. The Oregon Cattlemen’s Association will continue to advocate for legislation and government actions in furtherance of this goal, and assist members who are interested in exploring new or expanded water storage opportunities.
If you are interested, you might also check out Schroeder Law Offices’ free webinar about winter storage, available at: http://water-law.com/water-right-video-handbook-guide/.