The “Dark Side” of Water Efficiency: The Rise of Return Flow Injury

The adoption of efficient water technologies is identified as a goal under Oregon Water Resources Department’s (“OWRD”) 2017 Integrated Water Resources Strategy (https://www.oregon.gov/OWRD/programs/Planning/IWRS/Pages/default.aspx). For agricultural uses, weather-based irrigation, soil moisture controls, computer controlled irrigation, and piping and drip irrigation systems are being developed to substantially reduce the amount of water applied to land for the same use. At first glance, the adoption of efficient irrigation technology appears to be a “no-brainer” with few downsides. However, the problem can be more complex than it first appears.
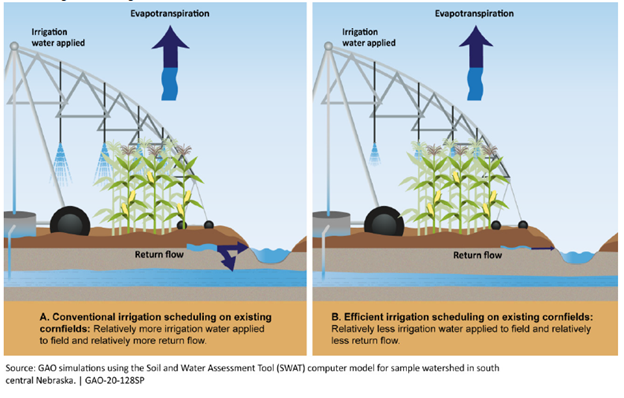
A core tenant of prior appropriation is the prevention of “injury” to existing water rights by reducing water available to fulfill existing rights of use. A component of a water right is the “consumptive use” or the amount of water for which the water user loses control usually from a described place of use or otherwise does not return to the source, the excess becomes available for subsequent use. Efficient irrigation technology alters irrigation’s consumptive use and runoff, sometimes reducing the water available to other water users that were benefitting from the “waste” created by inefficient irrigation techniques.
Often, inefficient irrigation seeps into shallow aquifers, sometimes contributing to surface streams days, months, or years later as return flow. Oregon’s conjunctive management rules have attempted to jointly regulate surface and groundwater sources, as described by Oregon Administrative Rules, Chapter 690, Division 9, yet these rules do not directly account for the effects of irrigation seepage on return flows. By encouraging efficient irrigation technologies, OWRD’s strategic planning might inadvertently cause injury to downstream water users that benefit from the increased return flow due to current irrigation techniques.
The United States Supreme Court (“Court”) addressed this issue in the case Montana v. Wyoming. 563 U.S. 368 (2011). The Yellowstone Compact distributes water of the Yellowstone River, which flows north from Wyoming into Montana. Water users in Wyoming adopted the use of more efficient sprinkler irrigation systems. The sprinklers increased the consumptive use portion of the water withdrawn compared to the earlier flood irrigation where a portion of the excess seeped into the ground. Montana alleged that the switch in technologies reduced seepage and runoff by 25% in some locations while still diverting the same quantity of water. In short, Montana lost access to water due to the increase in “efficiency” by Wyoming water users.
The Court decided that the switch did not cause injury to Montana water users, since these states appeared to only apply these rules to changes in “place of diversion, place or purpose of use” and not to changes in “crop changes or day-to-day irrigation adjustments or repairs.” The Court reasoned that a switch to efficient irrigation was more like an adjustment or repair than a change that would prompt the injury analysis. Likewise, the Court reasoned that the transition to sprinklers was akin to recapture doctrines under Wyoming and Montana, which allow water users to reuse water still remaining on their land after initial use. The Court reasoned that sprinklers are a form of efficient reuse of water rather than a fundamental change in water use supporting injury. The Court decided that Wyoming water users did not violate the Yellowstone Compact by using efficient irrigation technologies, even when significantly less water flowed to Montana.
The United States Government Accountability Office has recently released a report on irrigation technologies and their effects on return flows: https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-20-128SP?utm_campaign=usgao_email&utm_content=daybook&utm_medium=email&utm_source=govdelivery#summary. The report notes that efficient irrigation can expand the area of irrigation, enabling more production, using the same volume of water. At the same time, the report identifies that return flows might be significantly reduced and might diminish water availability for downstream users.
The key issue to consider is if water that seeps into an aquifer is considered a part of the consumptive use or whether it is returned to a source for further use. If consumption only includes the volume of water used by plants, other water users might have a right to the runoff from inefficient irrigation practices (which fits more with Oregon’s conjunctive management policies). If consumption is any water placed on the land without regard to the destination of the water applied, any reduction in return flow might not be considered an injury. As efficient irrigation practices are increasingly adopted, the dark side of decreased runoff might rise as a real issue in the future!
Make sure to stay tuned to Schroeder Law Offices’ Water Blog for more news that may affect you!





























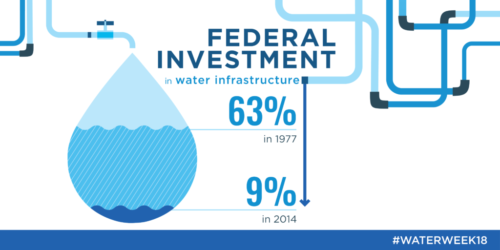 A few main events will take place during Water Week:
A few main events will take place during Water Week: 

