Oregon Department of Fish & Wildlife files for Instream Rights in Hood River Basin

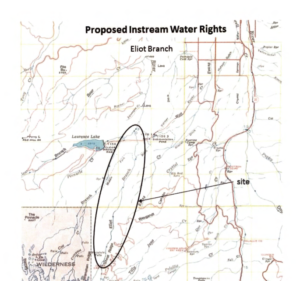
The Oregon Department of Fish & Wildlife (“ODFW”) filed applications for numerous instream water use rights in the last few months for salmon habitat in the Hood River basin. Instream water use rights in Oregon are held by state agencies for the preservation of a public purpose, like preserving salmon habitat. Beginning in December 1, 2016, ODFW began filing a series of applications with the Oregon Water Resources Department (“OWRD”) in the Hood River basin. The most recent applications were filled May 1, 2017.
ODFW filed similar instream water use applications in the past on various Oregon stream reaches. Such applications have been protested on the grounds that ODFW requested more water than is actually available from the source, that the amount of water requested is more than what is necessary for fish preservation and is not supported by data, injury to senior water users, detriment to the public interest, and more. The amount of water requested in the Hood River basin applications ranges from 10 cubic feet per second (“cfs”) to 175 cfs, depending on the application and time of year.
OWRD’s regulations allow instream water use rights to exceed the volume of water actually available at the source. Instream water use rights may be granted when a stream is already fully appropriated, although regulations state that instream rights may not exceed natural flows. Therefore, should senior water use rights be cancelled in the future, such cancellation would not free up water for new appropriations; rather, the cancelled water use rights would be swallowed by the ODFW instream rights that appropriate more water than is available at the source.
ODFW must provide scientific information used to determine the habitat needs supporting its water use applications. Two scientific methods were used in the recent applications. First, the quantities were determined using the Oregon Method, developed by Thompson in 1972, which determines the theoretical minimum needed for salmon spawning, adult passage, and rearing. (See http://www.dfw.state.or.us/fish/water/). The method focuses on the shallowest portion of a stream and determines the minimum flow required for salmon habitat needs. Using another study, habitat for the East Fork of the Hood River was determined using river modeling software. (See the draft report at http://www.co.hood-river.or.us/vertical/sites/%7B4BB5BFDA-3709-449E-9B16-B62A0A0DD6E4%7D/uploads/Appendix_C_Instream_Flow_Assessment_Draft_Report.pdf).
While the public comment period has passed for many of the applications, comments may still be submitted for the May 1, 2017 applications (Application Numbers IS 88336, IS 88333, IS 88332) after OWRD issues Initial Reviews for those applications. Anyone may comment on the applications within 30 days of the initial review and public notice. Additionally, protests may be filed after OWRD issues Proposed Final Orders for the applications, and additional applications may still be filed by ODFW.
Make sure to stay tuned to Schroeder Law Offices’ Water Blog for more news that may affect you!
This article was drafted with the assistance of Law Clerk Jakob Wiley, a concurrent student at Oregon State University’s Water Resources Policy and Management graduate program and a law student at the University of Oregon School of Law.